New Product Development (NPD) and New Product Introduction (NPI) for In-House Manufacturing
New Product Development (NPD) and New Product Introduction (NPI) are often mixed up or used interchangeably in industries. However, depending on the nature of the business and its product/service, these two processes are complementary and interconnected. The NPD is a comprehensive process that encompasses the entire lifecycle of a new product/service. Example: Moderna Vaccine for COVID-19. The NPI is a part of the NPD process that mainly focuses on testing and introducing a new product/service. It can also be standalone after the initial release of any innovative product/service. Example: The first iPhone release is through NPD Process, which includes NPI. Aftermarket success, each iPhone model release could be through a standalone NPI process focusing on validation and commercialization stages.
The NPD/NPI broadly describes transforming market opportunities into products/services that can be sold and produced profitably. Many tangibles (Industrial products) and intangible products (Technology-based services SaaS) can result from NPD/NPI. The process is a cross-functional, multi-discipline concurrent team approach for the development/introduction of a product/service. The strategy aims to address all interests across multiple departments and various business considerations to arrive at the best possible solution.
STAGES
NPD is a cyclic, flexible, and comprehensive process that accommodates the "fuzzy front end" of the development cycle, starting with the idea generation stage for a new product/service and continuing through the development, testing, and refining of the product/service. The NPI process is part of NPD, and it begins when the product/service features are settled, focusing mainly on the testing, validation, and commercialization stages. After that, it typically focuses on getting the product/service to market as quickly as possible while ensuring that it meets the target market's needs.
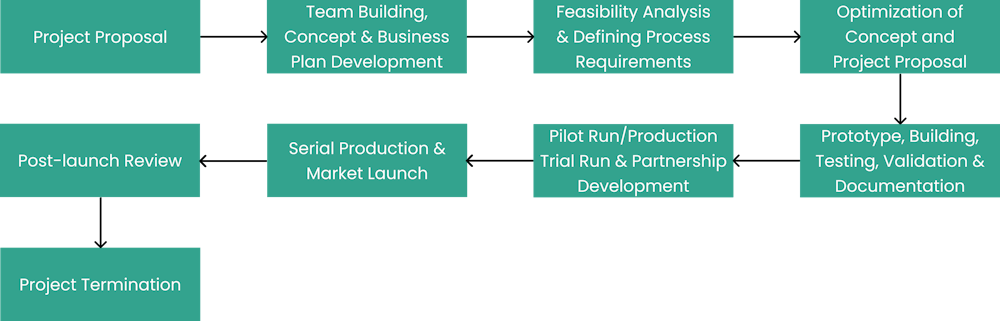
NPI/NPD Process is a set of business processes & techniques that would leverage a diverse group of people and co-create new value-added solutions, sustainable products/services, processes, and technology experiences. The objectives of the nine-stage gates and their deliverables are as follows:
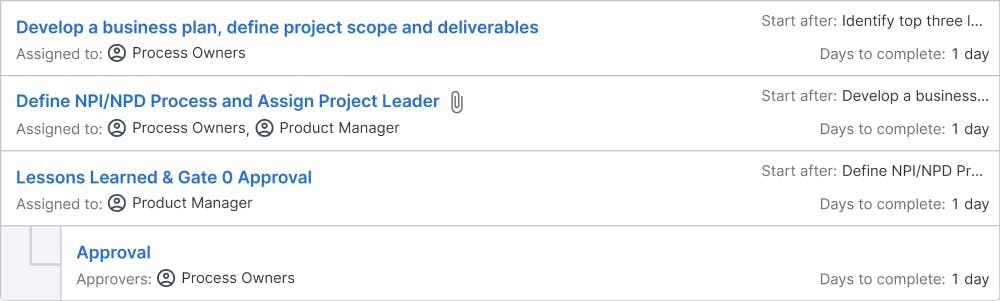
Project Proposal: defining new product/service needs, goals & opportunities
Objectives: Process Owners (executive team) collect new product/service and project ideas and evaluate them based on market information and business strategy. The focus is identifying customer needs (VOC), project goals, opportunities, and the market where the product/service will be sold. Based on the information, a list of project proposals to be further investigated will be prioritized, ranked, and assigned to a cross-functional core team responsible for product development.
Deliverables: a list of ideas, criteria for evaluating the ideas, process flow map, competitive market analysis, and business plan, Voice of Customer, Product/Service Requirements, Gate 0 Presentation
Team Building, Concept & Business Plan Development
Objectives: The cross-functional core team will develop the requirements and evaluate different concept design alternatives for feasibility. The product proposal is further refined into a concept drawing. An outsourcing plan is identified based on the chosen concept for the product. The team will prepare a regulatory checklist and market gap analysis. Finally, a business plan is developed with a schedule, risk management, and mitigation plan.
Deliverables: the cross-functional core team announcement, list of different concept designs, potential suppliers, customers, project charter, regulatory checklist, and market gap analysis. A final business plan with a schedule, risk mitigation plan, and Gate-1 presentation.
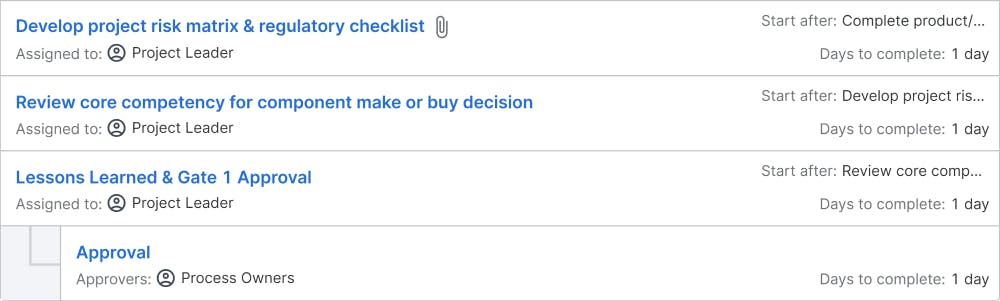
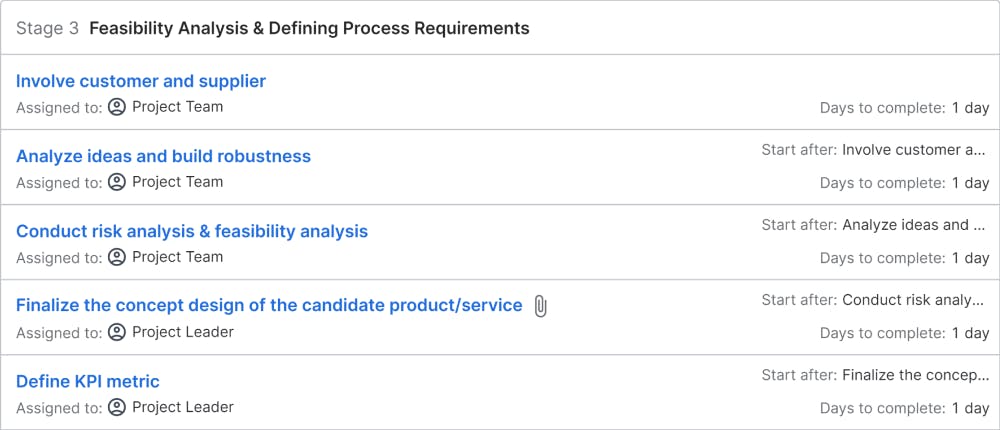
Feasibility Analysis. Customer & Supplier Involvement. Defining Process Requirements
Objectives: A conceptual review with customer input initiates project planning and supplier involvement. After the concept is approved, the project schedule is refined based on supplier involvement. The sweet spot between technical feasibility, customer desirability, and business viability will be identified in this stage. Finally, gate 2 is a Go or No-Go decision on the project based on the updated schedule, financial data, business analysis, and risk management plans.
Deliverables: feasibility analysis report, refined project schedule, Go or No-Go decision on the project, updated financial data, business analysis, risk management plans, updated regulatory checklist, prototypes, market research, refined product design, and Gate-2 presentation.
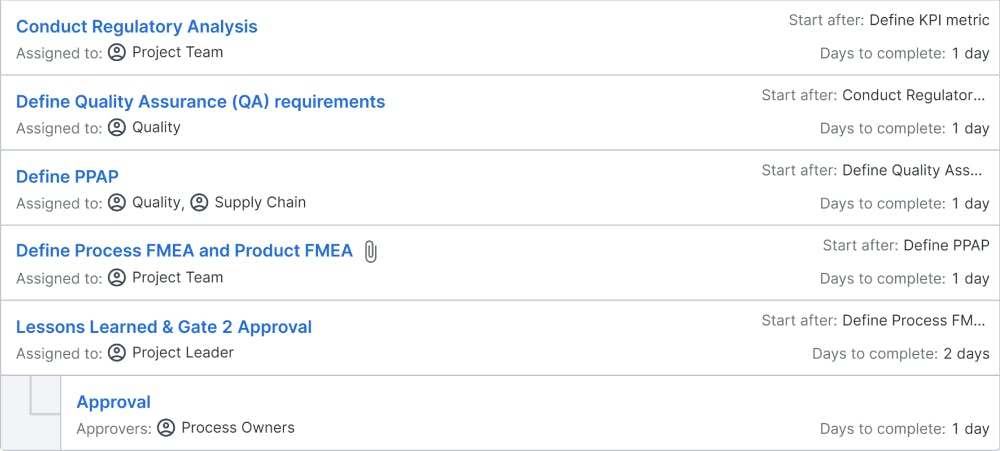
Optimization of Concept and Project Proposal. Development of Detailed Design, Specification & Costing
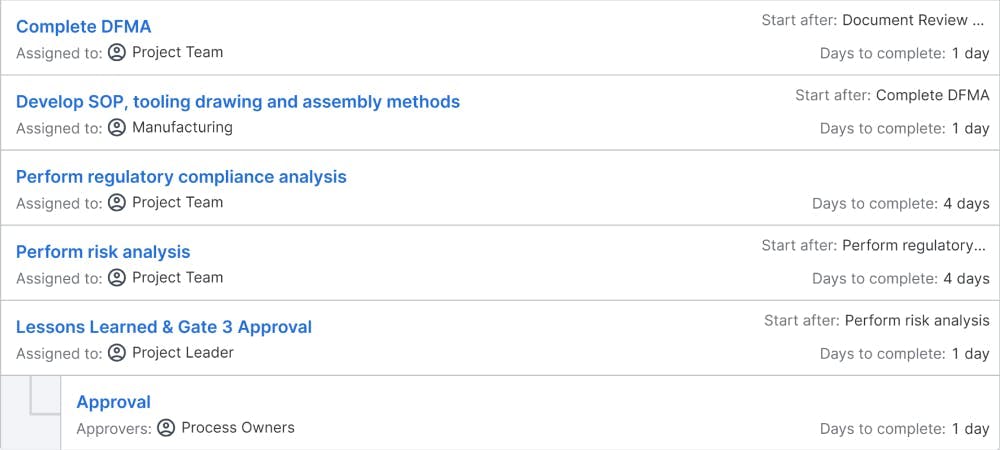
Objectives: Detail design & costing includes the generation of all necessary detail, BOM, assembly installation, and specification drawings to build prototype and production machines. Detail design provides for developing both product and process (SOP), DFMA, and FMEA. The system-level design review assesses whether the product meets the customer-identified product requirements. Preliminary versions of the manufacturing, marketing, and customer support documentation should also be completed in this phase.
Deliverables: detail design & costing includes the generation of all necessary detail, BOM, assembly installation, and specification drawings to build prototypes, tooling and production machines, Design Reviews, updated regulatory checklist, and risk mitigation plan, Product and process (SOP), and DFMA, FMEA. Preliminary versions of the manufacturing, marketing, and customer support documentation and the Gate-3 presentation.
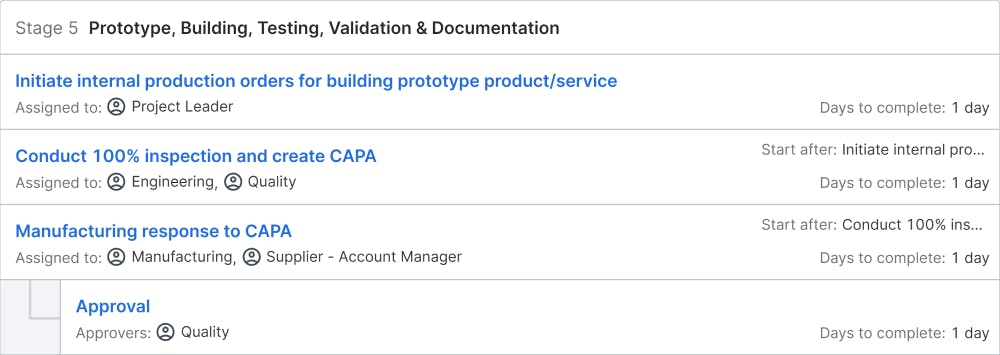
Prototype, Building, Testing, Validation & Documentation
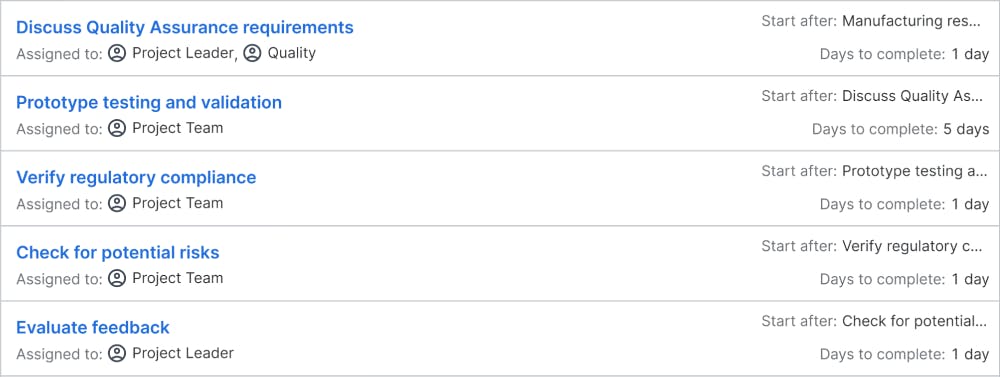
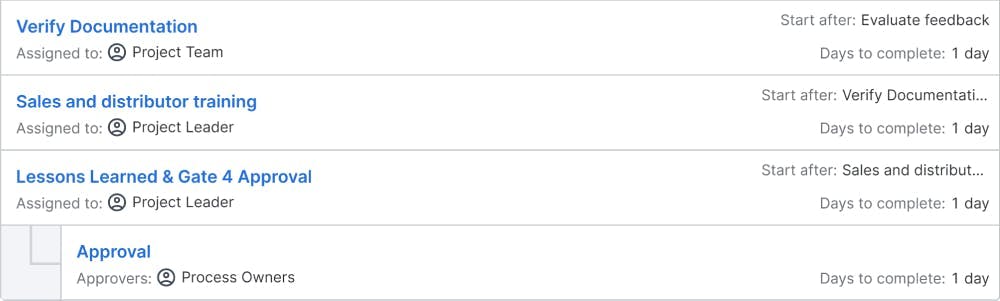
Objectives: Prototype build and test verifies the details of the documented new product/service, technical specifications, field support requirements, and manufacturing processes. This includes developing SOPs, tooling, process plans, assembly methods, building prototypes, and executing the test plan. In addition, support documentation for manufacturing, marketing, and customer service should be finalized. This stage concludes with sales and distributor training. Since the prototypes are sometimes made in different ways than mass production, they need to be more for defining and validating the manufacturing process.
Deliverables: the product/service is developed and tested in this phase. The deliverables for this phase include prototypes, test results, a refined product design, technical specs, SOPs, tooling, manufacturing methods, an updated regulatory checklist and risk mitigation plan, and Gate-4 presentation.
Market Testing: Pilot Run/Production Trial Run & Partnership Development
Objectives: compared to mass production, prototype products/services are not necessarily made with components, processes, equipment, people, and the production line. Before mass production, it is essential to define the manufacturing methods and the process. A few production runs (Pilot Runs) are made to test the line and ensure any significant issues are worked out. The Pilot Run is also called a product/service and process validation test. It involves transitioning to full-scale production on the manufacturing shop floor and operator training. The Pilot Run also verifies that the process can meet the quality requirements, assembly, and packing operations. Pilot Run products/services are sent to two or three loyal customers to perform field testing and obtain improvement feedback.
Deliverables: test results of relevant safety, quality, and functional performance obtained at the manufacturing/factory floor environment, validation test results obtained at the field/customers' job site, and their feedback on pilot products/services, updated regulatory checklist, and risk mitigation plan, and Gate-5 presentation.
Serial Production & Market Launch
Objectives: Commercialization brings a new product or service to market and makes it available for customers. In this stage serial production starts for launching and commercialization. This stage involves developing marketing and sales strategies, establishing a production plan, and preparing for product distribution. This includes loading serial production orders, running production, optimizing manufacturing techniques, reviewing costs, and monitoring warranty and quality issues. This last phase of the NPD/NPI cycle concludes with a project final report and NPD/NPI review.
Deliverables: marketing and sales materials, production and distribution systems, a launch plan, marketing and sales strategies, a production plan, cost analysis, report on warranty and quality issues, completed regulatory checklist and risk mitigation plan, NPD/NPI Project Final Report, and Gate-6 presentation.
Post-Launch Review
Objectives: the post-launch stage is the period after a product or service has been launched and is available for customers. In this stage, the product is monitored after its launch to assess its performance in the market, identify any problems or opportunities and determine any necessary improvements or changes. This stage typically involves market research, sales data analysis, and customer feedback surveys. Optimized manufacturing techniques and reported on costs, warranty, and quality issues.
Deliverables: In this phase, the product is monitored after its launch to assess its performance and identify any problems or opportunities. The deliverables for this phase include customer feedback, sales data, other metrics, and Gate-7 presentation.
Project Termination
Objectives: In this phase, the decision is made to continue supporting or terminate the product. This decision is typically based on the product's performance and the availability of resources. It also provides documentation of what the cross-functional team learned and unlearned during the whole process, celebrating the successes and moving to the next project.
Deliverables: the deliverables for this phase might include a decision memo, a plan for completing the product, a post-mortem analysis, final lessons learned report, NPD/NPI project closure report, and Gate-8 presentation.
WHY USE THIS PROCESS
Implementing the NPD/NPI Process can help companies stay competitive, satisfy customer needs, generate revenue, improve efficiency, and develop talent. Some advantages of the NPD/NPI Process managed by a cross-functional team are:
Innovation: Continuously allows companies to introduce new products/services and stay ahead of competitors. This can help them maintain a competitive edge and grow their market share.
Customer satisfaction: Help companies identify and address unmet customer needs, reduce lead time, and improves on-time delivery schedule leading to increased customer satisfaction.
Revenue generation: Supports strategic goals, improves market share and reduces development costs. This can help companies generate additional revenue streams and diversify their income sources.
Improved efficiency: Help companies streamline their production processes and improve efficiency, leading to cost savings and increased profitability.
Talent development: Provide opportunities for employees to develop new skills and expertise, which can help companies retain top talent and foster a culture of innovation.
Continuous Improvement: Support lean practices, standardization of product line, and help product safety and quality improvements.
Business relationship: Early integration with customers and suppliers and Pilot Run improve business relationships.
Team Building: Formal cross-functional team structure defines team empowerment and improves communication. Joint ownership among Marketing, Engineering, Operations, Quality, Finance, and Purchasing departments.
WHO SHOULD USE THIS PROCESS
Examples of industry products/services of NPD/NPI as follows:
NPD Product: Industrial products (machine tools and construction equipment), Consumer electronics, Tesla electric vehicles, Moderna COVID-19 vaccine, Tesla Solar Roof, Apple Watch.
NPI Product: Each new Model of the iPhone, as Apple develops and introduces new features and capabilities with each new release. Tesla electric vehicles Model S, Model 3, and Model X as Tesla develops and introduces new features and capabilities with each release.
NPD/NPI Service: Technology-based services (SaaS), Healthcare services, Hospitality and travel services, and Professional Services.
The new NPI/NPD process template is a good choice for Multinational/global businesses and in-house product manufacturing/service companies. It's an essential process for any company or business that wants to bring a new product/service to market or improve existing ones to meet changing needs. The multiple companies or businesses include technology, manufacturing, consumer goods, healthcare, and industrial. However, the process is ideal for the Original Design Manufacturing (ODM) Model due to IP protection and flexibility in changing the design. The size will be medium and large-size, with annual revenue above $500 million to $1 billion, having employees above 500. The NPD/NPI Process aims to ensure that all interests across multiple departments of any organization are addressed.
The process is designed as a generic version covering various aspects. It's flexible to use as part of a project-based or a standalone process. Depending on the size of the companies and the team's maturity, any stages/steps could be removed or skipped. It means the process can be customized so that even small companies with annual revenue of less than $500 million can be included. Once the process is set up in an organization, it can be used for qualifying future new products/services or continuous improvement for cost and quality optimization and significant upgrades of existing products/services.